
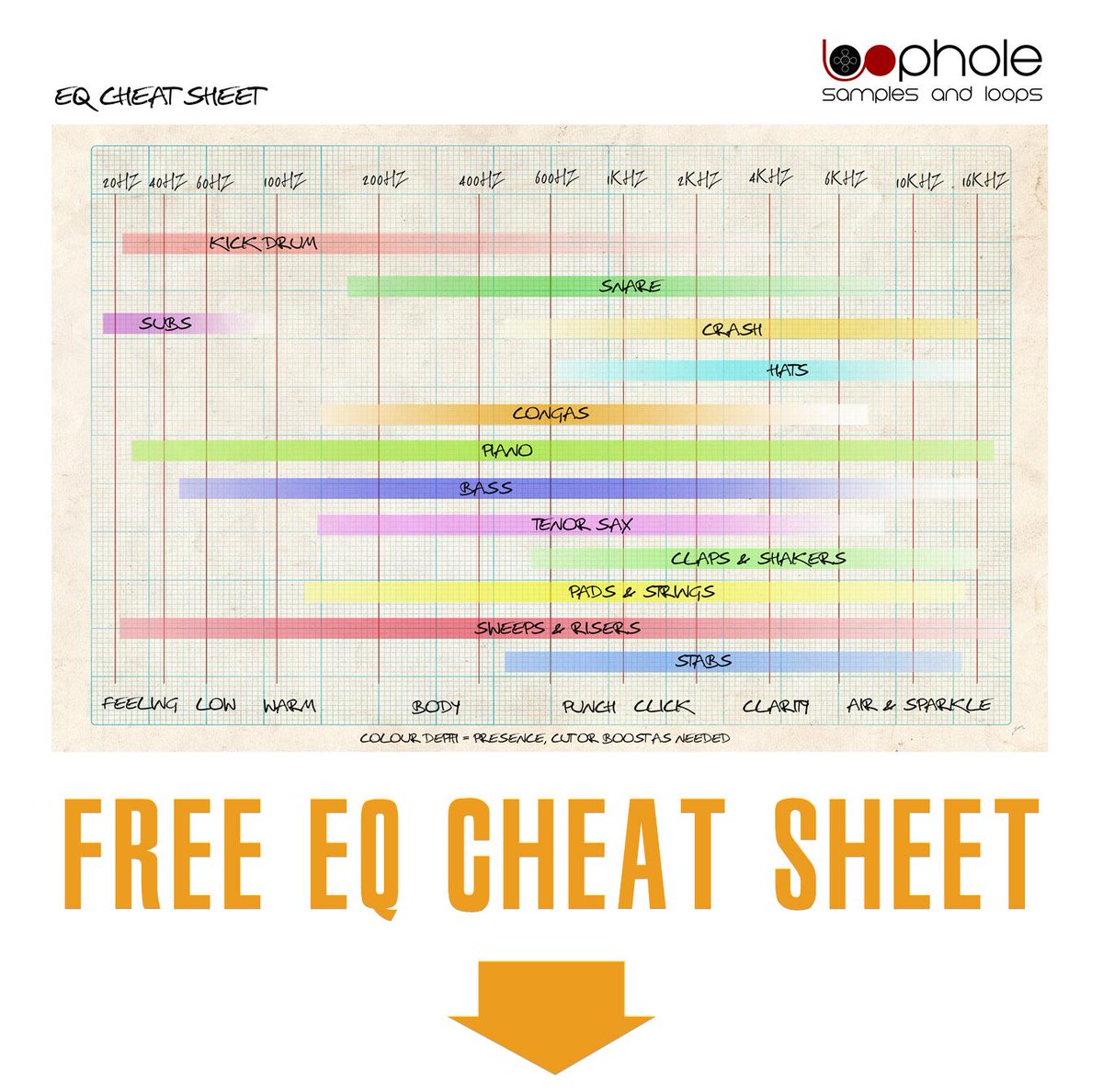
Virtually undetectable, you can safely cut these frequencies. Get my top tips for what frequencies I often cut or boost in certain sounds. Depending on what you're mixing the drums for, this range may vary. By frequency, by instrument with a glossary. A larger boost in this section will bring out the beater sound. If you have a hard time getting the kick drum to cut through the mix, don’t add more low-end, add more mids. Enter your first name and email address and click the Get Access Now The two basic types of recording in. Most metal kick drums have a cut at around 300 Hz.Ģ – 4 kHz – This is where the attack is. If boxiness is killing your kick drum sound, cut somewhere in this area. Cutting this are will give you more punch without adding more mud.ģ00 – 600 Hz – Here you'll find that cardboard sound. Waves Vocal Doubler/Pitch Shift Chorus Technique a. Send the vocal to the reverb and adjust the volume or EQ boost until you’ve reached the desired thickening 2. Equalization is one of the most difficult parts of recording to get the hang of since theres literally almost an infinite number of possibilities. They give the illusion of knowing where certain characteristics or. Look for a darker reverb to complement the warm EQ boost c. One of the biggest problems with EQ cheat sheets is that they are much too detailed. Don't boost too much because it can create a lot of mud in the low-end causing it to clash with other instruments in this frequency spectrum i.e bass guitar.ġ50 – 250 Hz – If you’re concerned about boosting the low-end too much, try cutting in this area. Create a new reverb send with an EQ that is boosted in the low-mids with cuts to the sub-bass and upper-mids b. 50 – 100 Hz – Boost this area to add low-end punch.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
